
Crohn's Disease - Expert Diagnosis & Management
Crohn's Disease
Comprehensive Management of Crohn's Disease
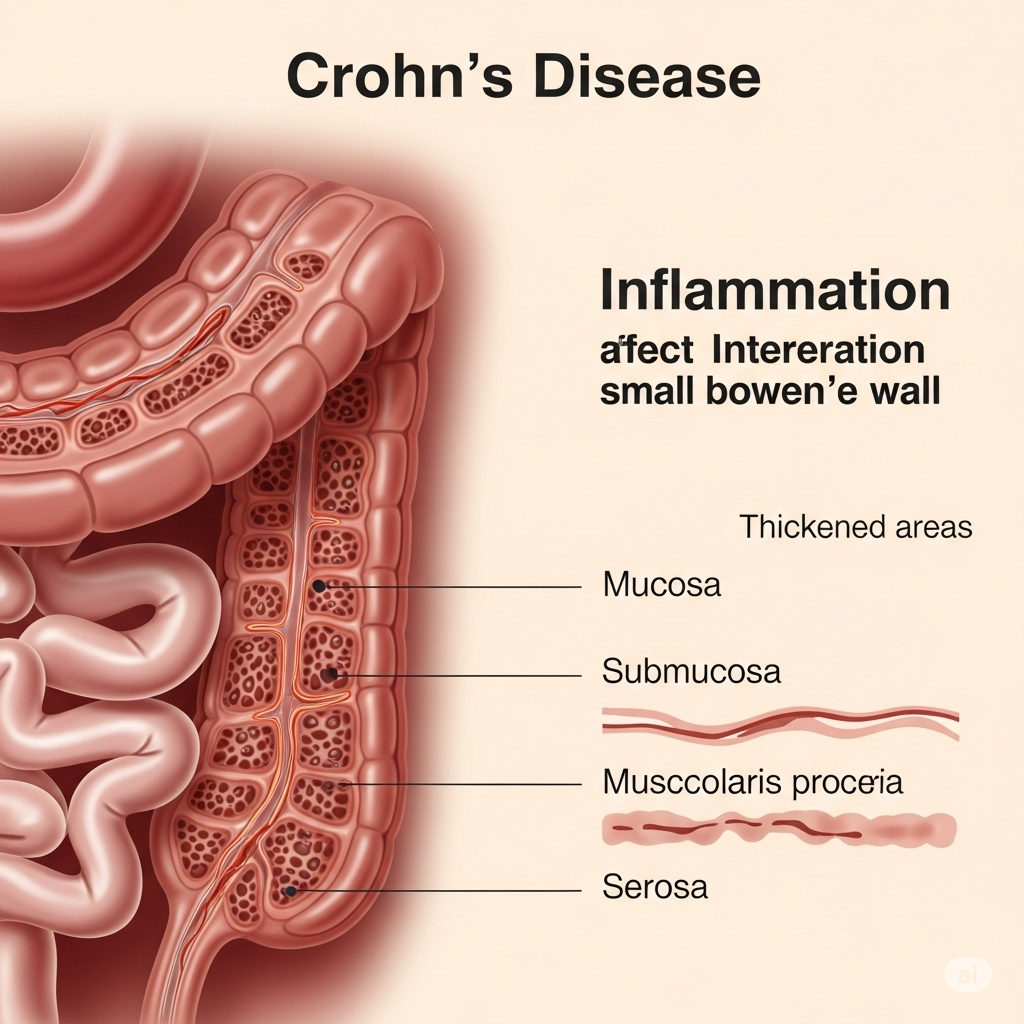
Crohn's Disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, from the mouth to the anus. Unlike ulcerative colitis, which primarily affects the colon, Crohn's disease can involve multiple segments of the digestive tract, often in patchy areas, and extends deep into the layers of the bowel wall. This chronic inflammation can lead to a range of debilitating symptoms and complications.
What is Crohn's Disease?
Crohn's disease is believed to be an autoimmune condition, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the digestive tract, leading to inflammation. While there is no cure, effective treatments can help manage symptoms, achieve remission, and prevent complications. The disease typically flares up and then goes into periods of remission.
Common Symptoms:
Symptoms of Crohn's disease vary depending on the affected part of the GI tract and the severity of inflammation. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping: Often localized, can be severe.
- Severe, persistent diarrhea: Sometimes with blood or mucus.
- Weight loss: Due to reduced appetite and malabsorption of nutrients.
- Fatigue: A common and often debilitating symptom.
- Fever: Indicating active inflammation or infection.
- Reduced appetite.
- Mouth sores.
- Perianal disease (e.g., fistulas, abscesses, fissures around the anus).
- Anemia (due to chronic bleeding or malabsorption).
Beyond the digestive tract, Crohn's can also cause extraintestinal manifestations, such as:
- Joint pain (arthritis).
- Skin issues (e.g., erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum).
- Eye inflammation (uveitis).
- Liver or bile duct inflammation.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact cause of Crohn's disease is unknown, but a combination of factors is believed to play a role:
- Genetics: A family history of IBD increases risk.
- Immune system: An abnormal immune response may cause the body to attack its own cells.
- Environmental factors: Diet, smoking, stress, and certain medications (like NSAIDs) may trigger or worsen the disease, but do not cause it.
- Gut microbiome: Imbalance in gut bacteria may contribute.
Diagnosis of Crohn's Disease:
Diagnosing Crohn's disease often involves a combination of tests to differentiate it from other conditions like IBS or ulcerative colitis:
- Blood tests: To check for inflammation, anemia, and nutritional deficiencies.
- Stool tests: To rule out infections and check for markers of inflammation.
- Endoscopy/Colonoscopy: To visualize the GI tract and take biopsies for microscopic examination. This is crucial for diagnosis.
- Capsule Endoscopy: To visualize the small intestine that traditional endoscopes cannot reach.
- Imaging tests: MRI (e.g., MR enterography), CT scans, or X-rays (e.g., barium studies) to detect inflammation, strictures, or fistulas.
Treatment and Management:
The goal of Crohn's disease treatment is to reduce inflammation, relieve symptoms, achieve and maintain remission, and prevent complications. Treatment plans are highly individualized and may include:
- Medications:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Aminosalicylates (5-ASAs), corticosteroids (for short-term control of flares).
- Immune system suppressors: Azathioprine, methotrexate, cyclosporine, to reduce inflammation by suppressing the immune response.
- Biologic therapies: Advanced medications (e.g., anti-TNF agents like infliximab, adalimumab; anti-integrins like vedolizumab) that target specific proteins involved in inflammation.
- Antibiotics: For infections, abscesses, or perianal disease.
- Anti-diarrheals and pain relievers: For symptom management.
- Dietary Modifications and Nutritional Support: While diet doesn't cause Crohn's, certain foods can worsen symptoms. Nutritional counseling, dietary adjustments (e.g., low-residue diet during flares), and supplements may be recommended.
- Surgery: May be necessary for complications like bowel obstruction, fistulas, or abscesses, or when medication is ineffective. Surgery aims to remove damaged sections of the bowel or repair complications.
- Lifestyle Management: Stress reduction techniques, smoking cessation (smoking significantly worsens Crohn's), and regular exercise can complement medical treatment.
Why Choose Dr. Neeraj Dhar for Crohn's Disease Treatment?
Dr. Neeraj Dhar is a leading gastroenterologist in Faridabad with extensive experience in the diagnosis and long-term management of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, including Crohn's Disease. He provides comprehensive and compassionate care, leveraging the latest advancements in IBD treatment. Dr. Dhar focuses on developing personalized treatment strategies that integrate medical therapies, dietary advice, and lifestyle modifications to achieve remission, manage symptoms, prevent complications, and significantly improve the quality of life for his patients living with Crohn's disease.
If you are experiencing symptoms suggestive of Crohn's disease, or if you are looking for advanced management of your existing condition, consult Dr. Neeraj Dhar for expert guidance and care.
