
Biliary & Pancreatic Stenting
- Advanced Endoscopy
- Upper GI Endoscopy
- Lower GI Endoscopy (Colonoscopy)
- ERCP (CBD Stone Removal / Stenting)
- EUS Guided Procedures (FNA/FNB, Drainage)
- Single / Double Balloon Enteroscopy
- Esophageal / Antral Stenting
- Esophageal & Anorectal Manometry
- Foreign Body Removal
- PEG Tube Placement
- POEM (Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy)
- STER (Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection)
- ESD (Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection)
- EMR (Endoscopic Mucosal Resection)
- Spyglass for Pancreatic Biliary Pathology
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Biliary & Pancreatic Stenting
- Anti Reflux Procedures
Stenting for Optimal Bile & Pancreatic Drainage
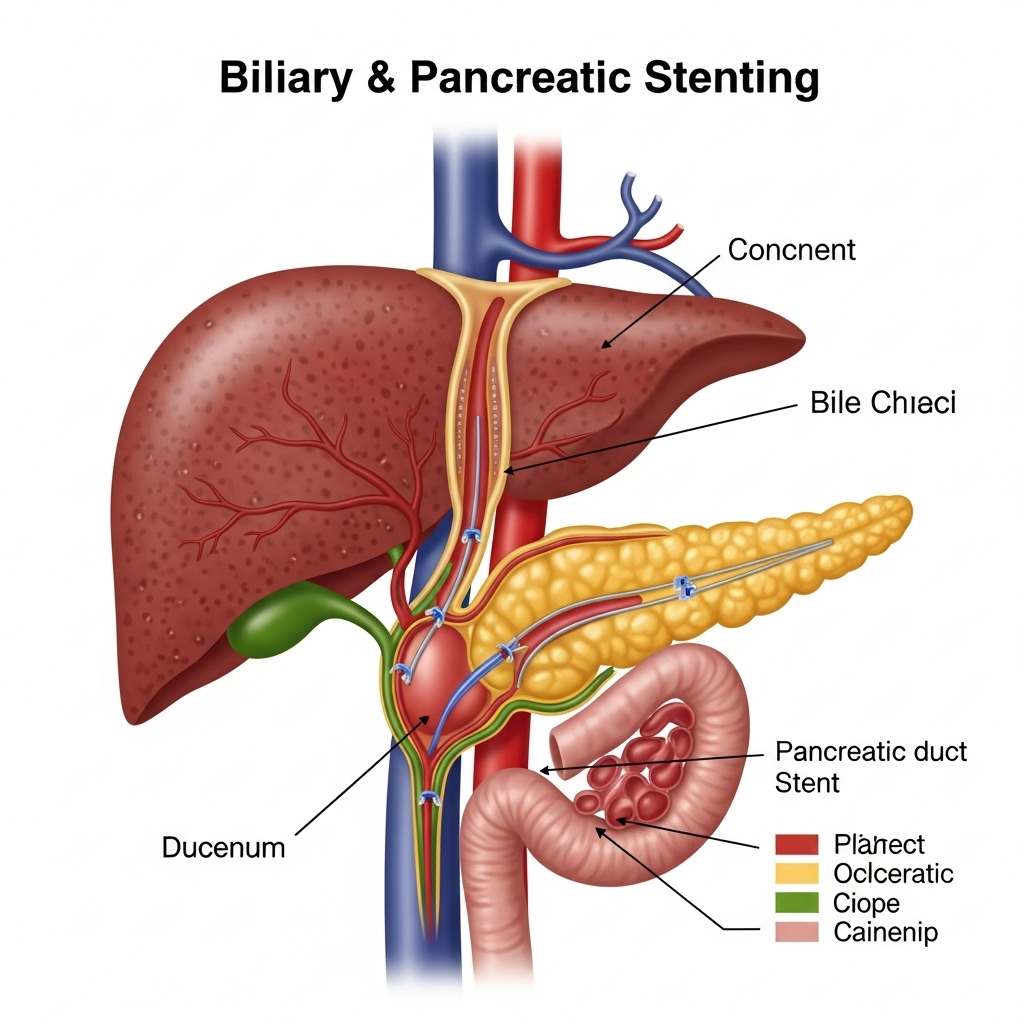
Biliary & Pancreatic Stenting: Restoring Flow and Relieving Obstruction
**Biliary and Pancreatic Stenting** is a crucial therapeutic endoscopic procedure performed by Dr. Neeraj Dhar to alleviate blockages or narrowings (strictures) within the bile ducts or pancreatic ducts. These blockages can lead to serious conditions like jaundice, infections (cholangitis), severe pain, and impaired organ function. Stents are small, hollow tubes placed inside the ducts to keep them open and ensure proper drainage of bile from the liver or digestive enzymes from the pancreas.
What are Bile Ducts and Pancreatic Ducts?
- Bile Ducts: A network of tubes that carry bile (produced by the liver to aid digestion) from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine.
- Pancreatic Ducts: Tubes that carry digestive enzymes (produced by the pancreas) to the small intestine.
When these ducts become blocked, fluids back up, causing symptoms and potential complications.
Causes of Blockages Requiring Stenting:
Blockages can be caused by various conditions, both benign and malignant:
- Gallstones: Stones that migrate from the gallbladder and lodge in the bile duct.
- Benign Strictures: Non-cancerous narrowings often due to inflammation (e.g., chronic pancreatitis), previous surgery, trauma, or certain inflammatory conditions.
- Malignant Strictures: Blockages caused by tumors, such as pancreatic cancer, cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer), gallbladder cancer, or metastatic cancer pressing on the ducts.
- Pancreatic Pseudocysts: Collections of fluid that can compress the pancreatic duct.
- Pancreatitis: Severe or recurrent inflammation of the pancreas can lead to ductal strictures.
Types of Stents Used:
- Plastic Stents: Often used for temporary drainage in benign conditions, or for initial drainage in malignant cases. They typically need to be replaced periodically.
- Metallic Stents (Self-Expandable Metal Stents - SEMS): Generally used for long-term or permanent drainage, particularly in malignant obstructions, as they have a larger diameter and stay open longer. They can be covered or uncovered.
How is the Procedure Performed? (ERCP-Guided Stenting)
Biliary and pancreatic stenting is performed during an Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
- Anesthesia & Endoscope Insertion: You will receive sedation or general anesthesia. A thin, flexible ERCP endoscope is gently passed through your mouth, esophagus, stomach, and into the duodenum, reaching the opening of the bile and pancreatic ducts (ampulla of Vater).
- Duct Cannulation: Using X-ray guidance, Dr. Dhar will carefully insert a small catheter and guidewire into the desired bile or pancreatic duct.
- Visualization & Intervention: Contrast dye is injected to obtain an X-ray image (cholangiogram or pancreatogram) of the ducts, clearly showing the location and nature of the blockage. If necessary, other interventions like stone removal, balloon dilation of the stricture, or tissue sampling may be performed first.
- Stent Placement: The chosen stent (plastic or metallic) is then advanced over the guidewire and precisely positioned across the narrowed segment of the duct. Once in place, the stent expands to create a clear pathway for fluid drainage.
- Confirmation & Withdrawal: Additional X-rays confirm accurate stent placement and adequate drainage. The endoscope is then carefully withdrawn.
Benefits of Biliary & Pancreatic Stenting:
- Relieves Symptoms: Effectively reduces jaundice, itching, pain, and symptoms of cholangitis or pancreatitis.
- Prevents Complications: Reduces the risk of serious infections and liver damage due to bile backup.
- Improves Quality of Life: Especially for patients with malignant obstructions, it can significantly improve comfort and enable further cancer treatments.
- Minimally Invasive: Avoids major surgery, leading to faster recovery times.
Recovery and Post-Procedure Care:
- You will be monitored in a recovery area until the effects of sedation wear off.
- Mild abdominal discomfort or a sore throat may occur, but usually subside quickly.
- You'll typically stay in the hospital for a short period (often overnight) for observation.
- Instructions regarding diet, activity, and signs of potential complications (e.g., severe pain, fever, chills) will be provided.
- For plastic stents, follow-up ERCPs will be needed for stent exchange or removal. Metallic stents generally stay longer, but their patency also needs monitoring.
Why Choose Dr. Neeraj Dhar for Biliary & Pancreatic Stenting?
Biliary and pancreatic stenting requires highly specialized expertise in advanced interventional endoscopy. Dr. Neeraj Dhar is an accomplished gastroenterologist in Faridabad with extensive experience in performing complex ERCP procedures, including precise stent placement. His proficiency in handling diverse cases, combined with access to advanced endoscopic technology, ensures optimal outcomes for patients facing challenging biliary and pancreatic duct obstructions. Dr. Dhar's meticulous approach minimizes risks and prioritizes patient safety and comfort throughout the procedure.
If you are experiencing symptoms of biliary or pancreatic duct obstruction, consult Dr. Neeraj Dhar for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan, including advanced stenting procedures.
